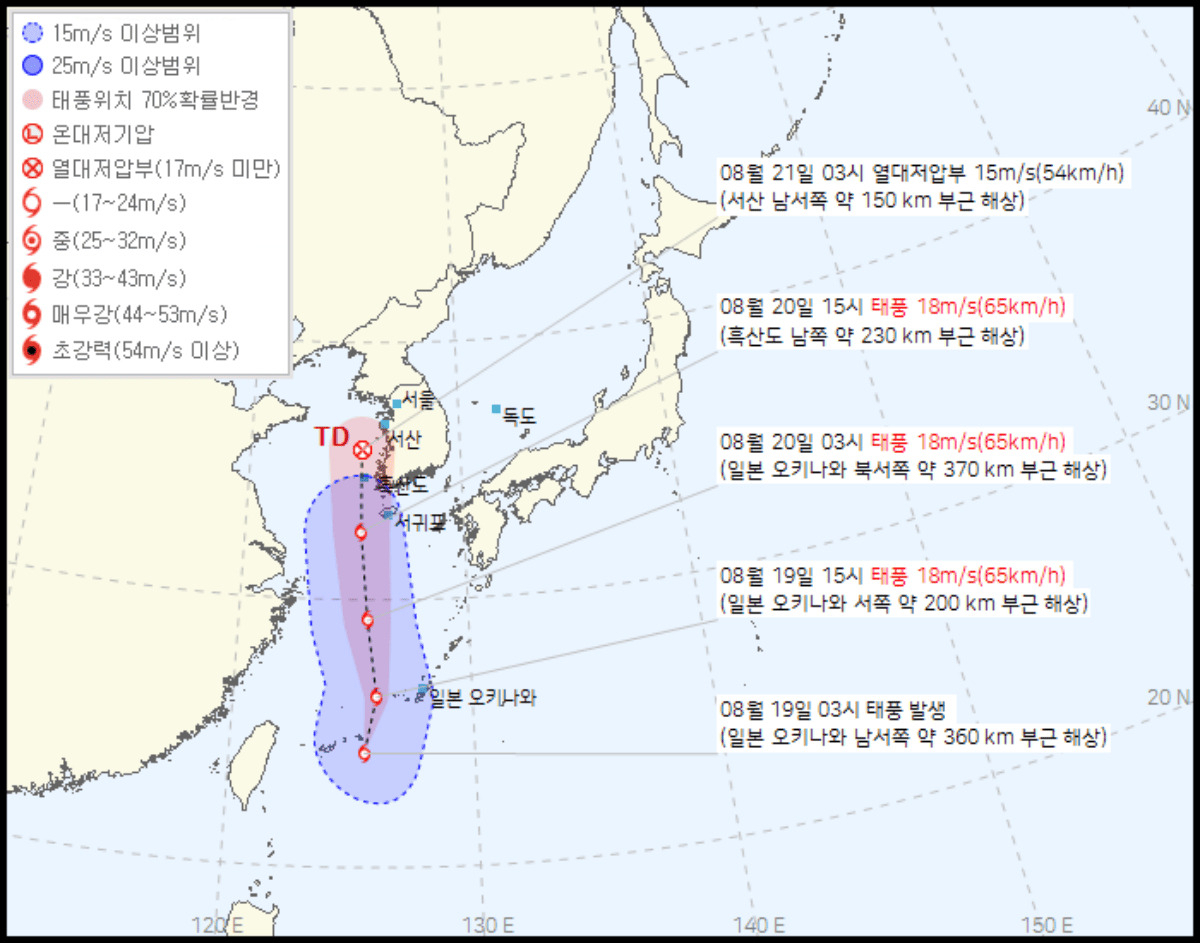
Typhoon Jongdari, the 9th typhoon of 2024, formed on August 19th in the waters southwest of Okinawa, Japan. This region is a common breeding ground for typhoons due to the combination of warm seawater and atmospheric instability, which create ideal conditions for typhoon formation. Jongdari initially developed in the East China Sea, gradually gaining strength as it moved northward. The formation process involved warm ocean temperatures and ample moisture in the atmosphere, leading to the development of a low-pressure system that eventually intensified into a typhoon.
As Jongdari advanced toward the Korean Peninsula, it continued to strengthen but is expected to weaken as it approaches the West Sea. Currently, the typhoon is moving north at approximately 28 km/h, with a central pressure of about 999 hPa and maximum winds of 65 km/h. The approaching typhoon is forecasted to bring heavy rains ranging from 30-80mm to southern regions of Korea, with some mountainous areas possibly receiving over 100mm. Additionally, wind speeds of 70-90 km/h are expected in Jeju and along the southern coast.
Though Jongdari is predicted to weaken as it nears Seosan in South Chungcheong Province around August 21st, it is still expected to bring significant rain and wind to southern Korea. The typhoon will also contribute to sustained heatwaves across the Korean Peninsula, as it pulls warm air from the south, maintaining the ongoing tropical nights and high temperatures.
The effects of Typhoon Jongdari on Korea are anticipated to be significant:
1. Strong Winds and Heavy Rain: As the typhoon moves north, Jeju Island and the southern regions will experience strong winds of 70-90 km/h and heavy rainfall, particularly in mountainous areas where over 100mm of rain could fall.
2. Storm Surges and Flooding: The combination of strong winds and high waves poses a risk of storm surges and flooding, particularly in coastal and low-lying areas.
3. Disruption of Transportation: The heavy rain and strong winds may cause flooding on roads and disrupt transportation, including the cancellation of flights and ferry services, especially in Jeju and the southern coastal regions.
4. Power Outages and Communication Disruptions: Strong winds could down power lines and damage infrastructure, leading to power outages and potential communication disruptions in affected areas.
5. Continued Heatwaves and Tropical Nights: The typhoon is likely to exacerbate the ongoing heatwave by drawing warm air from the south, leading to continued tropical nights and potentially higher energy consumption due to increased air conditioning use.
Monitoring the typhoon’s progress and preparing for its impacts will be crucial to minimize damage.



